Table of Contents |
The absolute value of a number is the distance from zero on the number line. Distance is never a negative value, so absolute value never returns a negative.
We can look at the number line and see that the absolute value of a positive number and the absolute value of a negative number are both positive:

Both -4 and 4 are 4 units away from zero on the number line. We can say that  and
and  .
.
This leads to a piecewise definition of absolute value:

This means that if x is zero or greater, the value of x does not change when we apply the absolute value. However, if x is negative, we change the sign of x when applying the absolute value, so as to make it positive.
When we solve any absolute value equation, we just remember that the expression can be positive or negative, and still have the same absolute value. For this reason, we create two separate equations: one with a positive value, and one with a negative value, for the expression inside absolute value bars:

|
|

|
Create two equations |

|
Our solution |
To solve absolute value equations, we can remove the absolute value bars only if we create two equations: one equation will look nearly identical to the original absolute value equation, while the second equation will consider the case when the expression is negative.
Next, we will consider more complex absolute value equations
Once again, we are going to solve this equation by creating two separate equations without absolute value bars. One equation will contain the expression exactly as it appears within the absolute value bars. The second equation must consider the case when the expression has the opposite value. That is, we reverse the sign on the other side of the equation:
EXAMPLE
Find the solutions to the absolute equation .
.

|
Create two equations |

|
Solve each equation |

|
Solve the first equation by subtracting 2 from both sides |

|
Divide both sides by 3 |
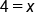
|
Our solution |

|
Solve the second equation by subtracting 2 from both sides |

|
Divide both sides by 3 |

|
Convert into a decimal |

|
Our solution |
 are
are  .
.
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License