In this lesson, you will learn how to evaluate a sum or difference with positive and negative numbers. Specifically, this lesson will cover:
1. Adding Positive and Negative Numbers
The ability to work comfortably with negative numbers is essential to success in algebra. For this reason, we will do a quick review of adding and subtracting positive and negative integers. Integers are all the positive whole numbers, zero, and their opposites (negative numbers).
When adding integers, we have two cases to consider. The first case demonstrates a situation with matching signs: both integers are either positive, or both integers are negative. If the signs match, we will add the numbers together, and keep the sign. This is illustrated in the following examples:

|
Same sign, add  keep the negative keep the negative
|

|
Our Solution
|

|
Same sign, add  keep the negative keep the negative
|

|
Our Solution
|
The second case demonstrates a situation with signs that don't match (one integer is positive and one integer is negative). We will subtract the numbers (as if they were all positive), and then use the sign from the larger number. This means if the larger number is positive, the answer is positive; and if the larger number is negative, the answer is negative. This is shown in the following examples:

|
Different signs, subtract  use sign from bigger number, negative use sign from bigger number, negative
|

|
Our Solution
|

|
Different signs, subtract  use sign from bigger number, positive use sign from bigger number, positive
|

|
Our Solution
|

|
Different signs, subtract  use sign from bigger number, positive use sign from bigger number, positive
|
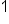
|
Our Solution
|

|
Different signs, subtract  use sign from bigger number, negative use sign from bigger number, negative
|

|
Our Solution
|
-
When adding two numbers with matching signs, add the two numbers (as if they are positive) and keep the sign. When adding two numbers with opposite signs, subtract the smaller number from the larger number (as if they are positive), and keep the sign of the larger number.
2. Subtracting Positive and Negative Numbers
For the subtraction of negative numbers, we will change the problem to an addition problem, which can then be solved using the above methods. The way we change subtraction to addition is to add the opposite of the number after the subtraction sign. Often this method is referred to as "adding the opposite." This is illustrated in the following examples:

|
Add the opposite of 
|

|
Different signs, subtract  use sign from bigger number, positive use sign from bigger number, positive
|

|
Our Solution
|

|
Add the opposite of 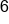
|

|
Same sign, add  keep the negative keep the negative
|

|
Our Solution
|

|
Add the opposite of 
|

|
Same sign, add  keep the positive keep the positive
|

|
Our Solution
|

|
Add the opposite of 
|

|
Different sign, subtract  use sign from bigger number, negative use sign from bigger number, negative
|

|
Our Solution
|
When adding and subtracting positive and negative numbers, it is important to pay attention to the sign of the numbers. When subtracting integers, it is often helpful to rewrite as an addition. To rewrite a subtraction problem as addition, change the sign of the number after the subtraction sign, and change the operation from subtraction to addition. Then, we can follow strategies for adding positive and negative numbers.

 keep the negative
keep the negative


 keep the negative
keep the negative


 use sign from bigger number, negative
use sign from bigger number, negative


 use sign from bigger number, positive
use sign from bigger number, positive


 use sign from bigger number, positive
use sign from bigger number, positive
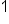

 use sign from bigger number, negative
use sign from bigger number, negative




 use sign from bigger number, positive
use sign from bigger number, positive


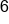

 keep the negative
keep the negative




 keep the positive
keep the positive




 use sign from bigger number, negative
use sign from bigger number, negative
