Table of Contents |
Adding and subtracting radicals is very similar to adding and subtracting with variables. Consider the following example:
EXAMPLE
Evaluate the following expression that has variables:

|
Combine like terms |
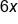
|
Our Solution |
EXAMPLE
Evaluate the following expression that has radicals:

|
Combine like terms |

|
Our Solution |
Notice that when we combined the terms with  it was just like combining terms with x. When adding and subtracting with radicals we can combine like radicals just as like terms. We add and subtract the coefficients in front of the radical, and the radical stays the same.
it was just like combining terms with x. When adding and subtracting with radicals we can combine like radicals just as like terms. We add and subtract the coefficients in front of the radical, and the radical stays the same.
EXAMPLE

|
Combine like radicals  and and 
|

|
Our Solution |
We cannot simplify this expression anymore as the radicals do not match. Often problems we solved have no like radicals, however, if we first simplify the radicals, we may find we do in fact have like radicals.
EXAMPLE

|
Simplify radicals, find perfect square factors. |

|
Take roots where possible |

|
Combine like terms |

|
Our Solution |
This exact process can be used to add and subtract radicals with higher indices. Indices is the plural of index, which indicates the type of root.
EXAMPLE

|
Simplify each radical, finding perfect cube factors. |

|
Take roots where possible |

|
Multiply coefficients |

|
Combine like terms 
|

|
Our Solution |
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License