Table of Contents |
There are several properties of radicals we can apply to simplify expressions involving radicals. The following properties are generally true whenever n is greater than 1, and 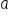 and b are both positive real numbers:
and b are both positive real numbers:
 and
and 



Avoid these common errors when applying properties of radicals:
 into two radicals
into two radicals  because
because  . However, we cannot break
. However, we cannot break  into
into  .
. as
as  because the exponent of 2 applied to everything underneath the radical. However,
because the exponent of 2 applied to everything underneath the radical. However,  This is because the exponent of 2 applies only to the x, not the 16. (We could rewrite the expression as
This is because the exponent of 2 applies only to the x, not the 16. (We could rewrite the expression as  because
because  )
)When we recognize products, quotients, and powers with radicals, we can apply the properties of radicals to simplify the expression.
EXAMPLE

|
Use Product Property of Radicals |

|
Evaluate: 
|

|
Simplify |

|
Our Solution |
EXAMPLE

|
Use Quotient Property of Radicals |

|
One factor of x cancels; one factor of y cancels |

|
Separate into two separate fractions |

|
Use Product Property of Radicals |
 
|
Use Quotient Property of Radicals and 
|

|
Simplify |

|
Our Solution |
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License