Table of Contents |
An application of linear equations can be found in distance problems. When solving distance problems we will use the relationship 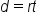 or distance equals rate (speed) times time.
or distance equals rate (speed) times time.

There are a couple of ways we can represent this relationship:
| Formula | Solve for... |
|---|---|

|
distance |

|
rate |

|
time |
The first example on how to use the distance-rate-time relationship is solving for distance.
EXAMPLE
Jason ran for 45 minutes, or 0.75 hours, at a speed of 7 miles per hour. How far did he run?
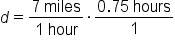
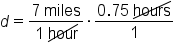
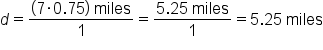
In this second example, we'll solve for rate.
EXAMPLE
Lee biked to his friend's house in 2 hours. He knows that his friend's house is 42 miles from where he started and he wants to know how fast did he bike.

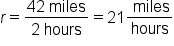
Finally, let's look at example where we solve for time.
EXAMPLE
Shira wants to rollerblade to the corner store. She knows she can rollerblade at 12 miles per hour and that the store is 4 miles away. How long will it take for her to get there?
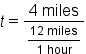
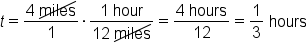
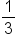 . It will take Shira
. It will take Shira 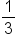 hours. If we want this fraction in minutes, we can just multiply it by the conversion factor,
hours. If we want this fraction in minutes, we can just multiply it by the conversion factor, 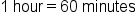 .
.
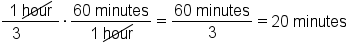
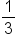 hours, or 20 minutes, to rollerblade 4 miles at a rate of 12 miles per hour.
hours, or 20 minutes, to rollerblade 4 miles at a rate of 12 miles per hour.
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License