Table of Contents |
The general journal is the initial documentation of a financial transaction as it originates. It contains transaction detail and accounting events in a chronological order.
Now, what are journal entries? Well, their name is derived from their use within the general journal. They are entries within the general journal and they detail the specific changes to accounts--the debits and credits.
If you recall, the first step in the accounting cycle is analyzing. If analysis determines that there is an accounting event, you move onto journalizing the transaction. There are no journal entries until accounting events have taken place.
Let's look at an example of a general journal, below. A general journal contains the following categories:

The general ledger aggregates all accounting records within an organization in preparation for financial statements.
The general ledger has a source document which is the general journal and all the journal entries within that general journal. The general ledger provides summary detail, data for all accounts, rolling totals, and information for the financial statements.
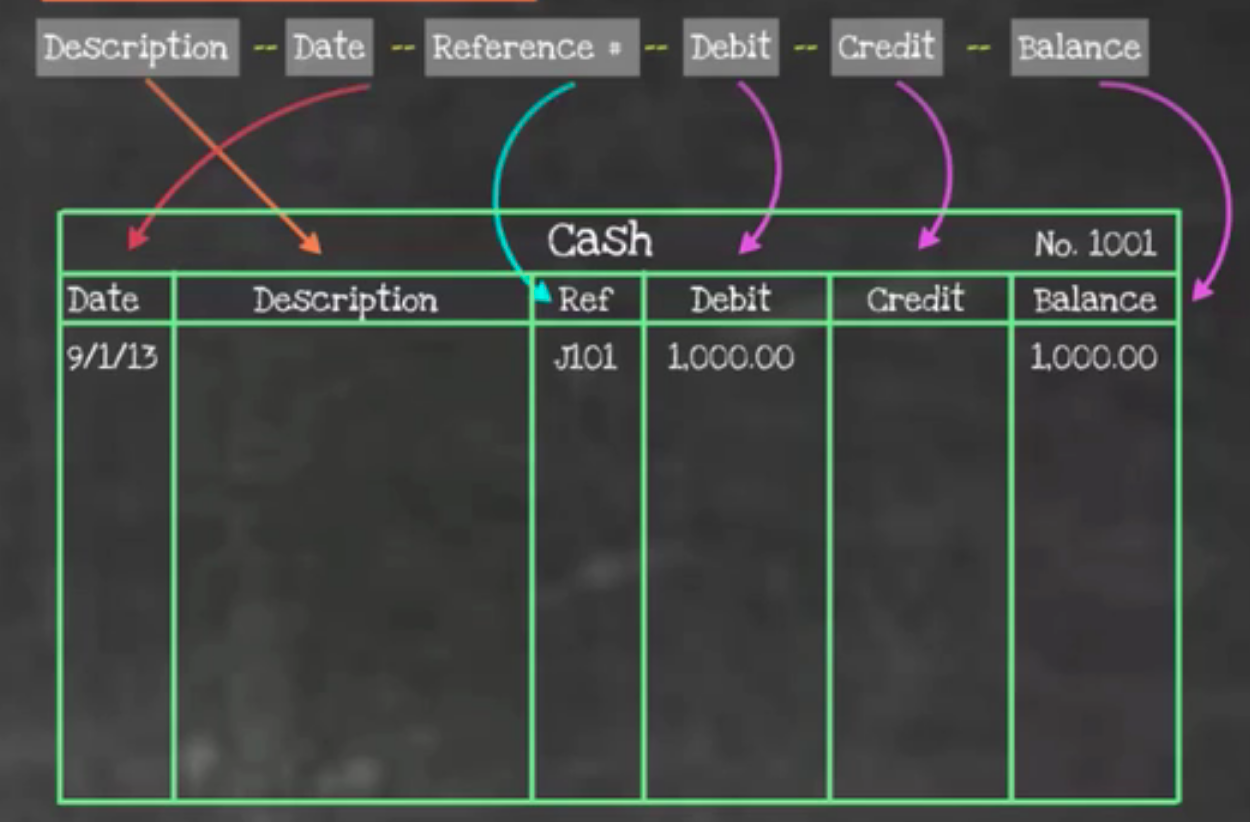
Let's look at an example of a general ledger, below. The general ledger has categories similar to a general journal, except that it also includes description and balance. As you can see, each individual account is going to have its own ledger. The example below is a cash ledger. You can see the identifier from the chart of accounts, No. 1001.
In a general ledger, you'd insert the date, the description, and the reference number, which in this case is going to refer back to the specific general journal and journal entry where the data points are coming from. It includes debits on the left and credits on the right, and it will also include any balance. In this example, you can see there is a debit to the cash account, so now there is a balance of $1,000.
So, how do the general journal and general ledger relate? Well, as mentioned, the general journal is an organizational tool and it is used to track detailed accounting events through the use of journal entries. It serves as the source for the general ledger.
Therefore, the general ledger gets its information from the general journal and those entries from the general journal are posted periodically, whether it's daily, weekly, monthly, or annually. Similar to the general journal, the general ledger is also an organizational tool to summarize accounting information.
Source: Adapted from Sophia instructor Evan McLaughlin.