Table of Contents |
Implantation occurs when an embryo attaches to the endometrium of the uterus. This process usually occurs between 9 to 12 days after fertilization. Recall that when a sperm cell fertilizes an oocyte, it becomes a zygote. The zygote cleaves, forming many cells from the single-celled zygote. When it forms 16 cells, it is a ball of cells called a morula. The morula forms a thin outer layer surrounding a fluid-filled cavity in which the inner cell mass will become the embryo—this formation is called a blastocyst.
During implantation, zona pellucida, which was previously enclosing the blastocyst, will break open. Then, the cells of the blastocyst's outer layer will attach to the connective tissue of the endometrium. Remember, the endometrium is the tissue lining the uterus, and this is occurring within the uterus.

Once the embryo has attached to the endometrium, it will start secreting human chorionic gonadotropin, abbreviated HCG. HCG stimulates the corpus luteum (the cells that are used to form the follicle nourishing the oocyte before ovulation) to secrete estrogen and progesterone. The continued secretion of estrogen and progesterone prevents menstruation (the shedding of the endometrium that nourishes the developing embryo).
If implantation has occurred, you don't want menstruation to occur because the embryo would be shed along with the lining of the uterus. Menstruation has to be prevented, which is accomplished by progesterone and estrogen being secreted by the corpus luteum. Generally, fertilization occurs within the fallopian tubes, and the fertilized egg will move into the uterus where development begins.
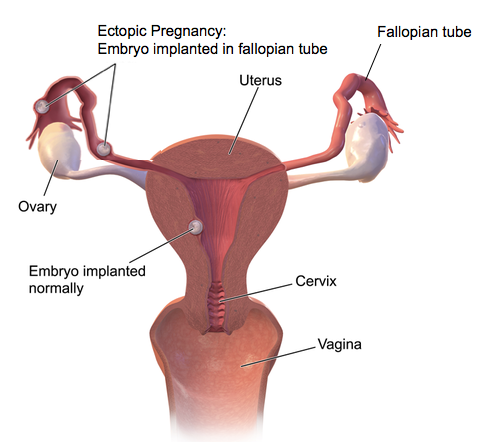
Sometimes pregnancies can occur within the oviduct. Rather than the egg moving into the uterus and developing there, the pregnancy can actually occur in the oviduct or fallopian tube. This is called an ectopic pregnancy or tubal pregnancy. Generally, those type of pregnancies cannot last and will lead to the death of the embryo and mother if medical intervention isn't taken.
Source: THIS WORK IS ADAPTED FROM SOPHIA AUTHOR AMANDA SODERLIND