Table of Contents |
In a function, the input variable undergoes one or more operations to yield a specific output value. We can think of this idea as x being the input to  where the output value is y. We can say that
where the output value is y. We can say that 
With inverse functions, the operations performed on the input variable are undone. This means that when y is put into the inverse function, the result will be the x value that produced y in the original function.
We can write this using inverse notation as: 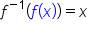
The above expression is telling us that if the value of a function,  goes into an inverse function,
goes into an inverse function,  the result will be the argument of the original function, x.
the result will be the argument of the original function, x.
 for inverse notation. Do not confuse the -1 with as an exponent.
for inverse notation. Do not confuse the -1 with as an exponent.
We can write an inverse function by applying inverse operations in reverse order, according to operations that make up a function.
EXAMPLE

|
Start with a number |
|
Multiply it by 2 |
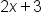
|
Add 3 to it |

|
Our function |

|
Start with a number |

|
Subtract 3 |

|
Divide by 2 |

|
Our inverse function |
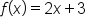 .
.
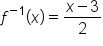 .
.
Operations for function, 
|
Operations for inverse function, 
|
|---|---|
| Start with x... | Starting with x... |
| 1) Multiply by 2 | 1) Subtract 3 |
| 2) Add 3 | 2) Divide by 2 |
Our solution: 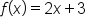
|
Our solution: 
|
There is symmetry between the graph of a function and its inverse. The line  acts as a line of reflection between a function and its inverse. This is characteristic of all functions and their inverses.
acts as a line of reflection between a function and its inverse. This is characteristic of all functions and their inverses.
EXAMPLE
Below is the graph of and
and  .
.

 is a line of reflection between a function and its inverse. This means that if you have the graph of a function, you can grab the line
is a line of reflection between a function and its inverse. This means that if you have the graph of a function, you can grab the line  , and use this line to plot points of the inverse function.
, and use this line to plot points of the inverse function.

 an input value undergoes one or more operations, resulting in an output value. If the resulting output value is the argument of the functions inverse, it will return to the original input value. The function,
an input value undergoes one or more operations, resulting in an output value. If the resulting output value is the argument of the functions inverse, it will return to the original input value. The function,  describes a set of operations done to an input, x. The inverse function and notation is
describes a set of operations done to an input, x. The inverse function and notation is  which describes the inverse operations of the original function
which describes the inverse operations of the original function  We can write an inverse function by applying inverse operations in reverse order, according to operations that make up a function. For the graph of a function and its inverse, the line, y equals x is a line of symmetry of the function and its inverse.
We can write an inverse function by applying inverse operations in reverse order, according to operations that make up a function. For the graph of a function and its inverse, the line, y equals x is a line of symmetry of the function and its inverse.
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License