Table of Contents |
The prefix "mono" means "one." A monopoly is a market that is controlled by a single company. A monocle is eyewear that consists of only one lens. Someone who speaks in a monotone voice tends to put people to sleep because the speak with a singular tone, with no variation in pitch.
In mathematics, a monomial is a single-term expression. Recall that a term is made up of a combination of numbers, variables, and powers.
EXAMPLE
The following are examples of monomials: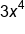
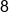
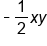

Note that there can be several variables in a monomial, as well as no variable at all. Coefficients can be fractional, positive, or negative. The important thing to notice is that there is no addition or subtraction. Addition and subtract separate terms, and since monomials only have one term, there is no need to separate multiple terms with addition or subtraction.
 is not a monomial.
is not a monomial.The prefix "poly" means "many." A polygon has many sides. A polytheistic religion believes in many deities. A polypeptide is a chain made up of several amino acids. A polynomial, then, is an expression with several terms.
EXAMPLE
The following are examples of polynomials: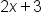
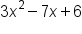
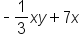
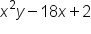
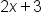 and
and 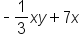 are binomials because they each have two terms.
are binomials because they each have two terms. 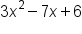 and
and 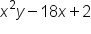 are trinomials because they each have three terms.
are trinomials because they each have three terms.Each term in a polynomial can be described by its degree, which is related to the exponent powers attached to variables in the term:
To find the degree of a term, simply find the sum of all exponents.
EXAMPLE
Find the degree of each term.| Term | Degree | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
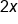
|
1 | The degree is 1 because the variable x has an implied exponent of 1. |
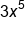
|
5 | The degree is 5 because the variable x has an exponent of 5. |

|
3 | The degree is 3 because the variable x has an exponent of 2, and the variable y has an implied exponent of 1. The sum of 2 and 1 is 3. |
It is standard to write terms in a polynomial by order of its degree, from highest to lowest. A reason for this is that we can also describe the degree of a polynomial. The degree of a polynomial is the same as the highest degree of all the terms. So when we have a polynomial written in order of descending degree, the first term also describes the degree of the polynomial.
EXAMPLE
Rewrite the following polynomial expression so that it is in proper order and also determine the degree: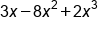
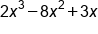
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License