Table of Contents |
Research is an essential part of higher education. Knowing how to conduct research, incorporate it into your writing, and properly cite it will be crucial to your success in your classes. Research is important because it familiarizes you with what experts in a specific field have to say about a certain topic. But, this is not just a passive exercise in collecting information. Incorporating research into your own work allows you to engage with those experts and join ongoing debates about your subject, contributing your own unique opinion.
Because research involves a synthesis of other people’s work and your own, it is necessary to cite your sources—that is, to give other people credit when you use their work. When you fail to cite your sources, that’s called plagiarism.
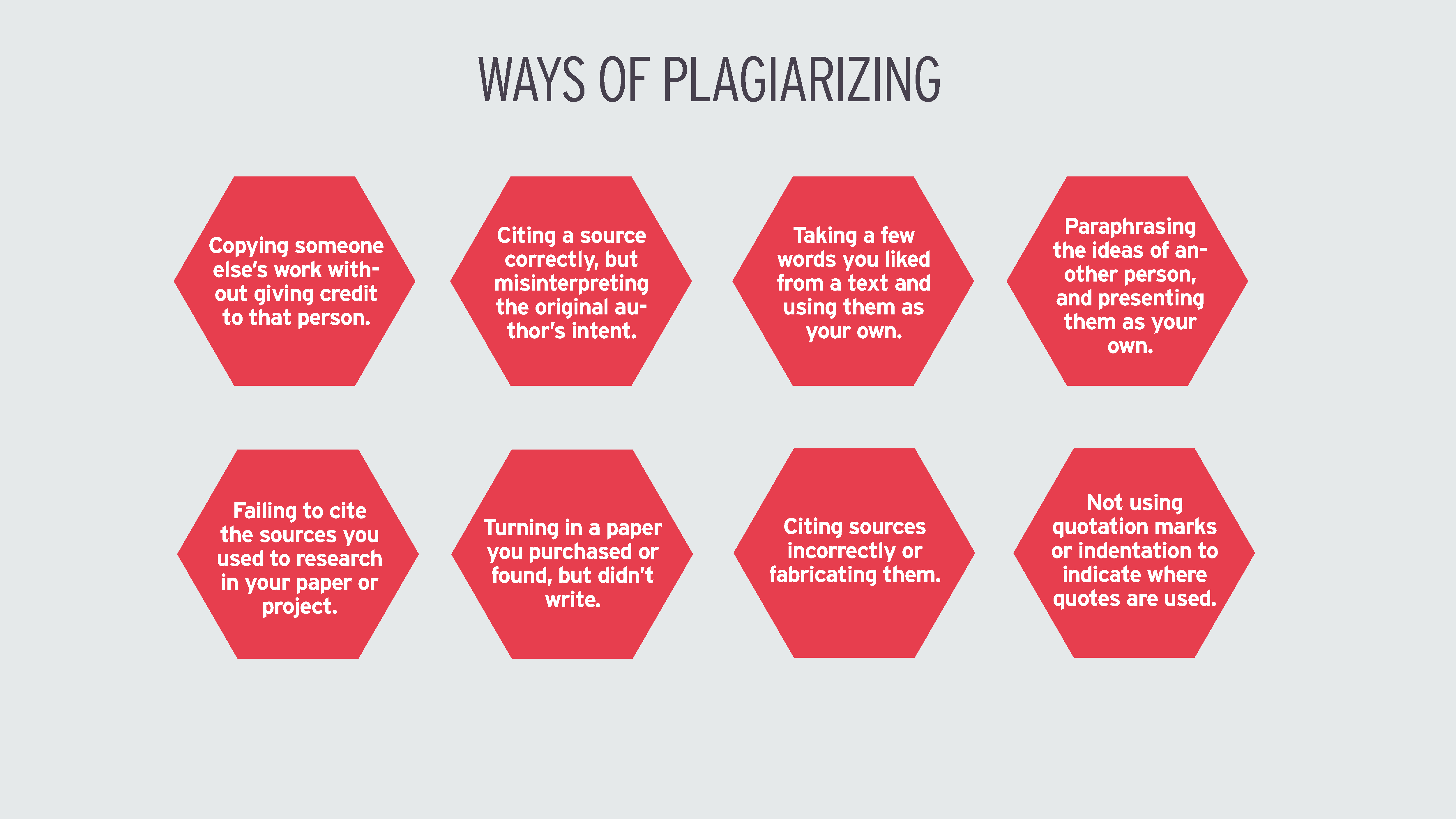
So how can plagiarism be defined? In the broadest sense, plagiarism means taking someone else’s words or ideas in your work and representing them as your own. Plagiarism is considered a violation of “academic honesty” because turning in plagiarized work amounts to lying about the source of your work and taking credit for ideas or words that don’t belong to you. Plagiarism can take many forms, so let’s have a look at some examples.
The emergence of AI-powered chatbots like ChatGPT has created a new type of plagiarism: copying and pasting the output of these chatbots and presenting it as your own. Even though you’re not stealing the work of another person, you’re committing an act of academic dishonesty if you turn in a paper or project written by AI. Because this technology is relatively new, the safest approach is to ask your instructor if there are specific rules about whether it’s ok to use AI technology at all in your course, and if so, in what ways.
The most common type of plagiarism these days is the “copy and paste” variety—the appropriation of articles found on the internet. There are a number of ways to go about it:
But plagiarism is not just the theft of the work of unsuspecting third parties whose work is published on the web. Other popular ways to plagiarize include turning in a paper you have purchased on the internet or having a friend write a paper for you.
IN CONTEXT
Given all this talk about the seriousness of plagiarism and its consequences, it would be understandable for a student to be wary and overly cautious when writing with research. Perhaps just to steer clear of academic dishonesty, a student might cite every bit of information that comes from an outside source.
But not everything needs to be cited. You don’t need to cite what’s considered common knowledge, such as facts that aren’t any particular author’s intellectual property. For example, you may have learned that Montpelier is the capital of Vermont by reading an article about food cooperatives, but you wouldn’t need to give credit to that author for having taught you that fact. It’s common knowledge, and now you share it.
People who submit plagiarized work may justify their actions to themselves in a few ways—they might claim they “had no choice” because they were so busy they couldn’t complete their assignment on time or that plagiarism is a harmless, “victimless” crime.
Plagiarism is never justified. If you are unable to submit your work on time, being honest with your instructor is a far superior course of action. And, in fact, plagiarism is not a “victimless crime”—it’s not only a kind of lying but also a kind of stealing. It’s dishonest to submit work that isn’t your own, but you are also taking someone else’s “intellectual property.”
Even though plagiarism is often committed casually, as if it’s “no big deal,” your institution takes it very seriously. Look up your school’s policies and procedures regarding academic honesty and familiarize yourself with them, as well as any information individual instructors provide on a course syllabus.
Plagiarism can result in a failing grade for an assignment, a failing grade for a course, or even expulsion from school. Many institutions require their instructors to report instances of academic dishonesty to the school.
In addition to the serious consequences, plagiarism is a risky proposition in that there’s a high probability of getting caught. In short, one thing is for certain—plagiarism is never going to be “worth it.”
Your instructor knows the difference between the writing typically turned in by students in a given course and the writing done by scholars in the field. In addition, your instructor to some extent knows you, your ability, and your own writing “voice.”
For these reasons, it is not difficult for your instructor to detect when phrasing is suspiciously sophisticated, inconsistent, or, in the case of AI-powered chatbots, bland and uninspired. And a quick Google search of the language in question will take them right to the source.
Even without the benefit of their well-trained eye for plagiarism, instructors these days have internet-based plagiarism-detection services like Copyleaks, Turnitin, or Grammerly, which scan your assignments and the internet for potential violations. Sites like these also allow you to check your work for potential plagiarism issues before turning in your paper or other written assignment.
In short, it's very easy for your instructor to figure out that you have plagiarized, which is another reason to avoid it.