Table of Contents |
This spinner has eight equally sized sectors. If you spin the spinner, there are three sectors marked with a 1, one marked with a 2, two marked with a 3, and another two marked with a 4. All the sectors are equally likely, but not every outcome is equally likely.

A probability distribution can be set up for the spinner. The probability distribution is a lot like a frequency distribution, except it will be set up as probabilities instead of frequencies. All the outcomes that could happen from the spinner will be listed.
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Next, instead of how often each number comes up in terms of frequency, we're going to list how often they come up in terms of probability. Three-eighths of the time you'll get a 1. One-eighth of the time you'll get a 2. Two-eighths of the time you'll get a 3, and two-eighths of the time you'll get a 4.
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability |

|

|

|

|
Two things should be noticed with this probability distribution:
1. Each individual probability must be between 0 and 1. 
Every probability--the three-eighths, one-eighths, two-eighths, etc.--is a number between 0 and 1. Any probability in a probability distribution has to be between 0 and 1 inclusive.
2. The sum of all probabilities must be 1. 
The sum of all the probabilities in the probability distribution is 1. It makes sense--with a probability of 1, it's certain that you will get a 1, 2, 3 or 4 on this spinner.
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability |

|

|

|

|

| ||||
This type of probability is called a discrete probability distribution, which means there are only so many outcomes.
| Possible Outcomes When Flipping Two Coins | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 
|
 
|
 
|
 
|
| Heads - Heads | Heads - Tails | Tails - Heads | Tails - Tails |
| Probability Distribution When Flipping Two Coins | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tails | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Probability |

|

|

|
The coin and spinner scenarios are both discrete probability distributions because there are only so many outcomes.
There are also probability distributions that are continuous probability distributions in which the probability is related by some mathematical function. For example, the normal distribution is a probability distribution.
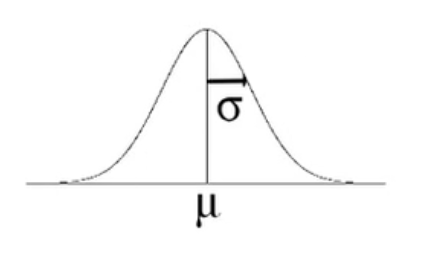
In this case, the area under the curve should equal one, and the graph should lie entirely above or on the x-axis. That's how those two rules apply to continuous distributions. With a continuous distribution, an outcome can be anything within this range on the x-axis.
It is important to note that some distributions have what we call countably infinite outcomes.
EXAMPLE
Suppose you are interested in the number of rolls it takes to obtain a 6 on your die. If you rolled a 6 on your first roll that would be a 1 because it took you one roll. If you rolled it on your second trial after missing on the first trial, then it would be a 2.
Source: THIS TUTORIAL WAS AUTHORED BY JONATHAN OSTERS FOR SOPHIA LEARNING. PLEASE SEE OUR TERMS OF USE.