Table of Contents |
In short, the commutative properties of addition and multiplication allow us to add algebraic terms in any order we wish, as well as multiply algebraic terms in any order we wish. These properties are illustrated in the following examples:
EXAMPLE
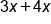
|
To simplify, add 4x to 3x |
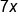
|
Sum of 3x and 4x |
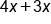
|
To simplify, add 3x to 4x |
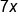
|
Sum of 3x and 4x |
EXAMPLE
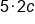
|
To simplify, multiply 5 by 2c |
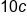
|
Product of 5 and 2c |

|
To simplify, multiply 2c by 5 |
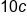
|
Product of 2c and 5 |
In each example above, notice that the order in which applied the operation (either addition or multiplication) did not affect the solution. It is important to note that subtraction and division are not commutative.
The associative property deals with how terms of an expression are grouped together. For algebraic expressions in which several terms are being added together, you can group terms together in any way in order to make simplification easier.
EXAMPLE

|
We can group terms in any way. Regroup  and and 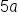 instead instead
|

|
Add  to to 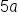
|
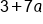
|
Our Solution |
In some cases, such as the example above, the associative property is helpful when grouping like terms together. We used the associative property first to add  and
and 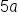 to get
to get  then we added 3 at the end.
then we added 3 at the end.
The associative property holds true for multiplication as well and works in a similar way to addition.
EXAMPLE
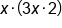
|
We can group terms in any way. Regroup x and 3x |
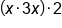
|
Multiply x and 3x |
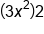
|
Multiply by 2 |
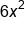
|
Our Solution |
Often as we work with problems, there will be a set of parentheses that make solving a problem difficult, if not impossible. To get rid of these unwanted parentheses, we can use the distributive property. Using this property, we multiply the number in front of the parentheses by each term inside.
EXAMPLE
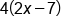
|
Multiply each term by 4 |
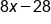
|
Our Solution |
EXAMPLE
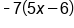
|
Multiply each term by 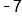
|
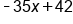
|
Our Solution |
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License