Table of Contents |
It is considered bad practice to have a radical in the denominator of a fraction. When this happens we multiply the numerator and denominator by the same thing in order to clear the radical. In the lesson on dividing radicals, we talked about how this was done with monomials. Here we will look at how this is done with binomials.
If the binomial is in the numerator the process to rationalize the denominator is essentially the same as with monomials The only difference is we will have to distribute in the numerator.
EXAMPLE

|
Want to clear  in denominator; Multiply both numerator and denominator by in denominator; Multiply both numerator and denominator by  to clear the radical in the denominator to clear the radical in the denominator
|

|
Distribute the  through the numerator, multiply the denominator by through the numerator, multiply the denominator by 
|

|
Evaluate any multiplication, ( ) )
|

|
Simplify radicals in numerator ( can be broken down to can be broken down to  ), multiply out denominator ), multiply out denominator
|

|
Take square root of 9 |

|
Reduce each term by 3 |

|
Our Solution |
If the binomial occurs in the denominator we will have to use a different strategy to clear the radical.
EXAMPLE
Consider . If we were to multiply the denominator by
. If we were to multiply the denominator by 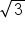 we would have to distribute it and we would end up with
we would have to distribute it and we would end up with  . We have not cleared the radical, only moved it to another part of the denominator. So our current method will not work.
. We have not cleared the radical, only moved it to another part of the denominator. So our current method will not work.
Instead, we will use what is called a conjugate. A conjugate is made up of the same terms, with the opposite sign in the middle. So for our example with  in the denominator, the conjugate would be
in the denominator, the conjugate would be 
The advantage of a conjugate is when we multiply them together, we have  , which is a difference and a sum. If we multiply these, we get a difference of squares. The final value ends up being the square of
, which is a difference and a sum. If we multiply these, we get a difference of squares. The final value ends up being the square of 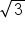 and the square of 5, with subtraction in the middle:
and the square of 5, with subtraction in the middle:

EXAMPLE

|
Want to clear radical from denominator; Multiply numerator and denominator by conjugate, 
|

|
Distribute numerator, difference of squares in denominator |

|
Evaluate multiplication in numerator and denominator |

|
Evaluate denominator |

|
Simplify solution by dividing by 2 |

|
Our Solution |
 . Both answers are correct.
. Both answers are correct.
EXAMPLE

|
Want to clear radicals from denominator; Multiply numerator and denominator by conjugate, 
|

|
Distribute numerator, difference of squares in denominator |

|
Evaluate multiplication in both numerator and denominator |

|
Simplify denominator |

|
Break down radicals:  can be broken down to can be broken down to  , ,  can be broken down to can be broken down to 
|

|
Take square roots where possible |

|
Our Solution |
The same process can be used when there is a binomial in the numerator and denominator. We just need to remember to FOIL out the numerator.
EXAMPLE

|
Want to clear radicals from denominator; Multiply numerator and denominator by conjugate, 
|

|
FOIL in numerator, difference of squares in denominator |

|
Evaluate multiplication in numerator and denominator |

|
Simplify denominator |

|
Numerator cannot be simplified any further; Divide each term by denominator, 1 |

|
Our Solution |
EXAMPLE

|
Want to clear radicals from denominator; Multiply numerator and denominator by conjugate, 
|

|
FOIL in numerator, difference of squares in denominator |

|
Evaluate multiplication in numerator and denominator |

|
Evaluate multiplication in denominator |

|
Evaluate subtraction in denominator; Cannot be simplified any further |

|
Our solution |
 is just
is just  We just use the opposite sign in between the two terms. The conjugate of just a radical by itself is that same radical.
We just use the opposite sign in between the two terms. The conjugate of just a radical by itself is that same radical.
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License