Table of Contents |
In review, a quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the following form, where a, b, and c are real numbers:

Factoring, or variable isolation, may be used to solve some quadratic equations, but not all. The quadratic formula, however, can be used to find solutions to all quadratic equations, even when factoring or variable isolation is difficult or impossible. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to use the quadratic formula to find solutions to a quadratic equation.
You may recall that the quadratic formula states that the solution(s) to a quadratic equation, x, are equal to:
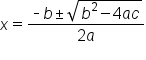
The values for a, b, and c in the quadratic formula come from the values of a, b, and c in the quadratic equation. The plus-minus symbol here indicates that a quadratic equation may have two solutions.


EXAMPLE
Suppose you want to solve the quadratic equation:
 , meaning that there is an implied coefficient of 1. Therefore, a equals 1. You can also see that b equals 7 and c equals -4.
, meaning that there is an implied coefficient of 1. Therefore, a equals 1. You can also see that b equals 7 and c equals -4.



 is 49, and 4 times -1 is -16. You now have 49 minus -16, which is the same as 49 plus 16, which equals 65. The square root of 65 cannot be further simplified, so you’d leave it as written.
is 49, and 4 times -1 is -16. You now have 49 minus -16, which is the same as 49 plus 16, which equals 65. The square root of 65 cannot be further simplified, so you’d leave it as written.




Source: This work is adapted from Sophia author Colleen Atakpu.