Table of Contents |
Recall that an algebraic expression is a combination of numbers, variables, and operators representing a quantity. When working with algebraic expressions, you should be familiar with the parts that make up the expression.

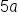

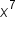 multiplied by one another. We can also dissect the expression a little further we get
multiplied by one another. We can also dissect the expression a little further we get 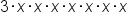 . Notice how all numbers and variables are combined through multiplication only. So we can say that the above examples represent a single term.
. Notice how all numbers and variables are combined through multiplication only. So we can say that the above examples represent a single term.
EXAMPLE
Suppose we have the expression . Define the parts of this algebraic expression:
. Define the parts of this algebraic expression:





When dealing with algebraic expressions the number of different terms that are added to or subtracted from one another give the expression a different name. Here we will look at different types of expressions based on the number of unique terms they contain.
A single algebraic expression with no other terms added to or subtracted from it is called a monomial.
EXAMPLE
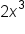 is a monomial.
is a monomial.
Typically when writing algebraic expressions we refer to them using their variable and the power the variable is being raised to.
EXAMPLE
 would be called a second-degree monomial because the variable is being raised to the second power.
would be called a second-degree monomial because the variable is being raised to the second power.
More complex types of algebraic expressions contain more than one monomial and are combined through either addition or subtraction.
If we have two monomials combined with one another through addition or subtraction, we call that expression a binomial.
EXAMPLE
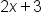 and
and 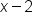 are binomials.
are binomials.
If we have more than two monomials combined with one another, we have what is called a polynomial.
EXAMPLE
 is a polynomial. We typically say that this expression is a second-degree polynomial because the highest power of any variable in the expression is 2.
is a polynomial. We typically say that this expression is a second-degree polynomial because the highest power of any variable in the expression is 2.
EXAMPLE
If we had the expression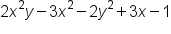 , we would count the total number of powers in each monomial to determine the power. In this example, we would say that this is a 3rd-degree polynomial because in the term
, we would count the total number of powers in each monomial to determine the power. In this example, we would say that this is a 3rd-degree polynomial because in the term 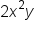 the combined power of x and y add up to 3.
the combined power of x and y add up to 3.
| Type of Algebraic Expression | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | A number |
4 12 157 |
| Monomial | One term |
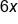  8xy |
| Binomial | Two terms |
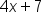  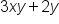
|
| Polynomial | More than two terms |
 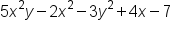 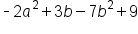
|
One way we can simplify expressions is to combine like-terms. Like-terms are terms where the variables match exactly (exponents included). Examples of like-terms would be 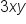 and
and  , or
, or 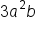 and
and  , or -3 and 5. If we have like-terms, we are allowed to add (or subtract) the numbers in front of the variables, then keep the variables the same.
, or -3 and 5. If we have like-terms, we are allowed to add (or subtract) the numbers in front of the variables, then keep the variables the same.
EXAMPLE
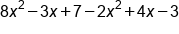
|
Combine like terms 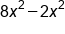
|
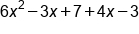
|
Combine like terms 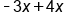
|
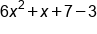
|
Combine like terms 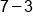
|
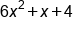
|
Our Solution |
EXAMPLE

|
Combine like terms 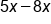
|
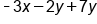
|
Combine like terms 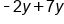
|
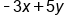
|
Our Solution |
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License