Table of Contents |
In math, an operation is a way to combine numbers, as in addition or subtraction. You can think of an operation in math as a calculation between two or more numbers.
There needs to be an agreed upon order for performing operations so that when there are several operations in an expression or an equation, everyone simplifies or solves in the same way to get the correct answer. Therefore, the order of operations is the rule that tells you the order in which to perform those operations.
The correct order of operations is Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction, otherwise referred to by the acronym PEMDAS.
You can use the order of operations to simplify an expression.
EXAMPLE
Suppose you want to simplify the expression: .
.

|
Our Expression |

|
Start with division; divide 4 by 2. |

|
Next is addition and subtraction from left to right; first, add 10 and 2. |

|
Finish by subtracting 1 from 12. |

|
Our solution |
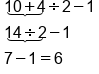
PEMDAS is the acronym you can use to remember the order of operations. PEMDAS stands for:
Parentheses
Exponents
Multiplication
Division
Addition
Subtraction
There are several important things to remember when using PEMDAS:
EXAMPLE
Suppose you want to simplify the following expression: .
.

|
Our Expression |

|
Evaluate the equation inside of the parentheses; 7 minus 5 is 2. |

|
Next, we calculate the exponent;  is 4. is 4.
|

|
Now, we move onto multiplication; 3 times 2 is 6. |

|
Finally, addition and subtraction from left to right; 8-4 is 4. |

|
Add 4 and 6 to get 10. |

|
Our solution |
The second example involves simplifying an expression containing negative numbers and exponents.

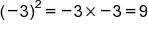

Now that you know how to avoid this common mistake, try using this knowledge when solving the equation in the second example.
EXAMPLE
Suppose you want to simplify the following expression: .
.

|
Our Expression |

|
Evaluate the exponent;  (the negative in front is like a negative 1 being multiplied, so you do not include it in your exponent operation). (the negative in front is like a negative 1 being multiplied, so you do not include it in your exponent operation).
|

|
Next we move onto multiplication and division, moving from left to right; 12 divided by 2 is 6. |

|
Multiply 6 by 3, which is 18. |

|
Add negative 16 and 18. |

|
Our solution |
Source: This work is adapted from Sophia author Colleen Atakpu.