Table of Contents |
The quadratic formula is used to solve quadratic equations that are written in standard form 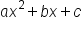 and set equal to zero. It uses the coefficients
and set equal to zero. It uses the coefficients  b, and c that are found in the standard equation. The quadratic formula is:
b, and c that are found in the standard equation. The quadratic formula is:
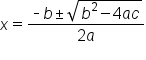
It looks like a complete mess, doesn't it? It can be a complicated formula to work through, but it is extremely useful in finding precise solutions to quadratic equations.
 .
.
As we saw in a previous lesson, one of the easiest ways to solve quadratic equations is to factor the expression and use the Zero Factor Property.
EXAMPLE
Find the solutions for the quadratic equation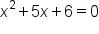 .
.
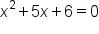
|
Find two integers that multiply to 6 and add to 5 |
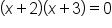
|
Use the Zero Factor Property and set each factor equal to zero |
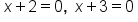
|
Evaluate |
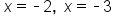
|
Our solutions |
However, consider a more complicated quadratic equation where it cannot be solved easily with factoring:
EXAMPLE
Find the solutions for the quadratic equation .
.
| p | q | sum: p + q |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -10 | -9 |
| -1 | 10 | 9 |
| 2 | -5 | -3 |
| -2 | 5 | 3 |
The quadratic expression in this example is known as a prime quadratic. Prime quadratics cannot be written in factored form, which means that factoring and solving using the Zero Factor Property is out of the question. In such cases, when we either cannot factor or are having trouble figuring out how to factor it, we can use the quadratic formula.
The quadratic formula can also tell us if there is a real solution to the quadratic equation. The expression underneath the radical is called the discriminant of the expression. Since it is underneath a square root, it must have a non-negative value to result in a real number.
When using the quadratic formula to solve a quadratic equation, use these steps:
 .
. b, and c.
b, and c. and
and 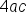 , then find the difference. This is called the discriminant.
, then find the difference. This is called the discriminant. This is one solution for x.
This is one solution for x. This is the other solution for x.
This is the other solution for x.Let's use the quadratic formula to solve the following equation:
EXAMPLE
Find the solutions to the quadratic equation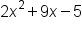 .
.
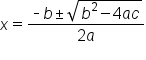
|
Identify the values for  b, and c in the equation b, and c in the equation 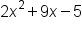
|

|
Substitute these values in the quadratic formula |
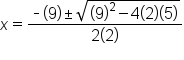
|
In the discriminant, square 9 and multiply 4, 2, and -5 |

|
Find the difference in the discriminant |
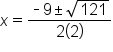
|
Evaluate the square root of 121 |

|
Create two solutions, one with addition and one with subtraction |
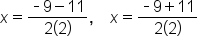
|
Evaluate |
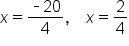
|
Simplify |
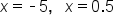
|
Our solutions |
Let's look at a little more complicated problem.
EXAMPLE
Find the solutions to the quadratic equation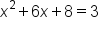 .
.
 b, and c to use in the quadratic formula. Remember, the equation needs to be set equal to zero before we begin to find solutions. Always be sure to check that your equation is set equal to zero. If it's not, we simply add or subtract terms from both sides of the equation, until zero is on one side of the equation, and everything else is on the other. For this specific equation, simply subtract 3 from both sides to get zero on the right side.
b, and c to use in the quadratic formula. Remember, the equation needs to be set equal to zero before we begin to find solutions. Always be sure to check that your equation is set equal to zero. If it's not, we simply add or subtract terms from both sides of the equation, until zero is on one side of the equation, and everything else is on the other. For this specific equation, simply subtract 3 from both sides to get zero on the right side.
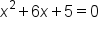
 b, and c.
b, and c.
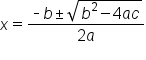
|
Identify the values for  b, and c in the equation b, and c in the equation 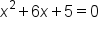
|

|
Substitute these values in the quadratic formula |
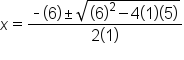
|
In the discriminant, square 6 and multiply 4, 1, and 5 |
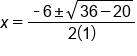
|
Find the difference in the discriminant |
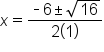
|
Evaluate the square root of 16 |
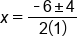
|
Create two solutions, one with addition and one with subtraction |
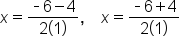
|
Evaluate |
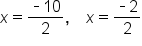
|
Simplify |
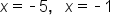
|
Our solutions |
 b, and c that are found in the standard equation. Prime quadratics cannot be factored because there are no two integers that will multiply to the constant term c and add to the b coefficient. Using the quadratic formula can be helpful in finding the solutions to x. When solving equations using the quadratic formula, the equation needs to be set equal to zero and then use the coefficients for
b, and c that are found in the standard equation. Prime quadratics cannot be factored because there are no two integers that will multiply to the constant term c and add to the b coefficient. Using the quadratic formula can be helpful in finding the solutions to x. When solving equations using the quadratic formula, the equation needs to be set equal to zero and then use the coefficients for  b, and c. If the value of the discriminant (b squared minus
b, and c. If the value of the discriminant (b squared minus 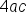 ) is negative, the equation has no real solution. If the value of the discriminant is non-negative, the equation has at least one real solution.
) is negative, the equation has no real solution. If the value of the discriminant is non-negative, the equation has at least one real solution.
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License