Table of Contents |
Consider the following geometric sequence: 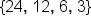 . To find the sum of this finite sequence, it is simple enough to concretely add together all of the terms:
. To find the sum of this finite sequence, it is simple enough to concretely add together all of the terms:


In this formula:
 is the sum of n terms
is the sum of n terms is the value of the first term
is the value of the first term is the common ratio
is the common ratio is the number of terms
is the number of termsEXAMPLE
Using the geometric sequence above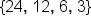 , confirm that the sum of the four terms above is 45 by using the formula as well.
, confirm that the sum of the four terms above is 45 by using the formula as well.
 ,
,  , and
, and  :
:
 : The first term is 24.
: The first term is 24.  : The common ratio can be found by dividing any two consecutive numbers:
: The common ratio can be found by dividing any two consecutive numbers:  .
.  : There are 4 terms, so
: There are 4 terms, so  is 4.
is 4.

|
Plug in 
|

|
Evaluate the exponent |

|
Simplify the numerator and denominator |

|
Evaluate the fraction |

|
Multiply |

|
Our solution |
Our formula works for any value of  , although when we are working through the calculations, it may seem as though something must be off. Don't worry, as long as you follow the steps properly, you should arrive at the correct sum.
, although when we are working through the calculations, it may seem as though something must be off. Don't worry, as long as you follow the steps properly, you should arrive at the correct sum.
EXAMPLE
Find the sum of the geometric sequence .
.
 ,
,  , and
, and  :
:
 : The value of the first term is 32.
: The value of the first term is 32. : The common ratio is 1.5, which is found by dividing any two consecutive terms, such as
: The common ratio is 1.5, which is found by dividing any two consecutive terms, such as  .
. : Since we have 5 terms in the sequence,
: Since we have 5 terms in the sequence,  .
.

|
Plug in 
|

|
Evaluate the exponent |

|
Simplify the numerator and denominator |

|
Evaluate the fraction |

|
Multiply |

|
Our solution |

The formula even works if the common ratio is a negative number.
EXAMPLE
Find the sum of the geometric sequence .
.
 ,
,  , and
, and  :
:
 : The first term is 6
: The first term is 6 : Here, the common ratio is -3, because we multiply 6 by -3 to get -18, -18 by -3 to get 54, and so on.
: Here, the common ratio is -3, because we multiply 6 by -3 to get -18, -18 by -3 to get 54, and so on.  : There are 5 terms so
: There are 5 terms so 

|
Plug in 
|

|
Evaluate the exponent |

|
Simplify the numerator and denominator |

|
Evaluate the fraction |

|
Multiply |

|
Our solution |

We can even use the formula to find a partial sum of a geometric sequence. A partial sum means that we add some of the terms in the sequence, but not all of them.
EXAMPLE
Find the sum of the terms 3 through 8 in the geometric sequence with 12 terms:
 : We will consider
: We will consider  to be 52. Although it is the 3rd term in the sequence, it is the 1st term we wish to include in the sum.
to be 52. Although it is the 3rd term in the sequence, it is the 1st term we wish to include in the sum. : The common ratio is 2, since
: The common ratio is 2, since 
 : We will use
: We will use  because the sum of terms 3 through 8 consists of 6 terms altogether: 3rd term, 4th term, 5th term, 6th term, 7th term, and 8th term.
because the sum of terms 3 through 8 consists of 6 terms altogether: 3rd term, 4th term, 5th term, 6th term, 7th term, and 8th term.

|
Plug in 
|

|
Evaluate the exponent |

|
Simplify the numerator and denominator |

|
Evaluate the fraction |

|
Multiply |

|
Our solution |

 is the first term in the sequence, r is the common ratio between consecutive terms, and n is the number of terms. The formula for finding the sum of a finite geometric sequence can be used when r is both positive and negative, or the geometric sum when r is greater than 1 or r is less than 0. The formula can also be used to calculate a partial sum of a finite or infinite sequence.
is the first term in the sequence, r is the common ratio between consecutive terms, and n is the number of terms. The formula for finding the sum of a finite geometric sequence can be used when r is both positive and negative, or the geometric sum when r is greater than 1 or r is less than 0. The formula can also be used to calculate a partial sum of a finite or infinite sequence.
Source: ADAPTED FROM "BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA" BY TYLER WALLACE, AN OPEN SOURCE TEXTBOOK AVAILABLE AT www.wallace.ccfaculty.org/book/book.html. License: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License